 Dec. 19, 2023
Dec. 19, 2023
Injection molding is the most cost-effective way to make a plastic part at scale. The injection molding process involves injecting molten plastic into a mold tool, then ejecting the solidified part. This article gives a simple introduction for the mold structure and the principles of it.
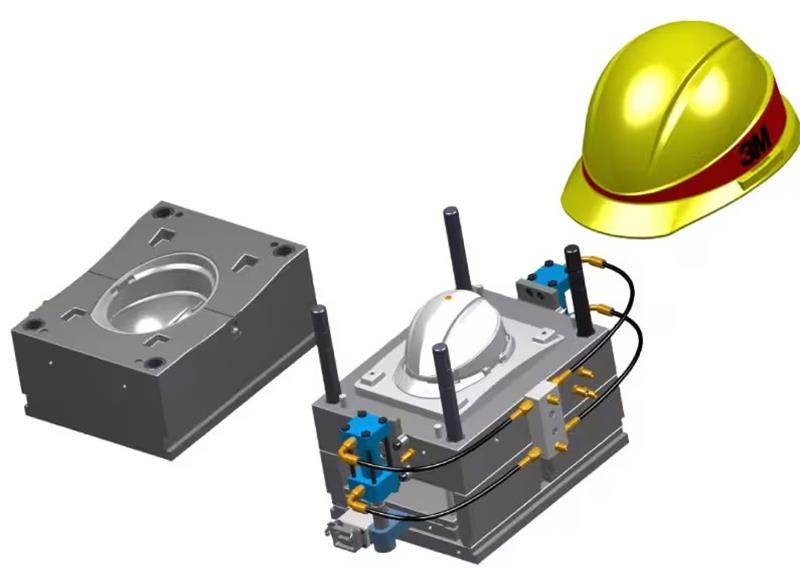

Fig.1 Mold and Part
Different plastic products exhibit varying mold structures due to differences in plastic types, product shapes, structures, and the type of injection molding machine. However, their basic structures remain consistent.
In essence, an injection mold comprises two components: the moving mold and the fixed mold. The moving mold is responsible for opening before injection completion, preparing to eject or retrieve the product. The moving part during mold opening is termed the moving mold, while the stationary part is the fixed mold.
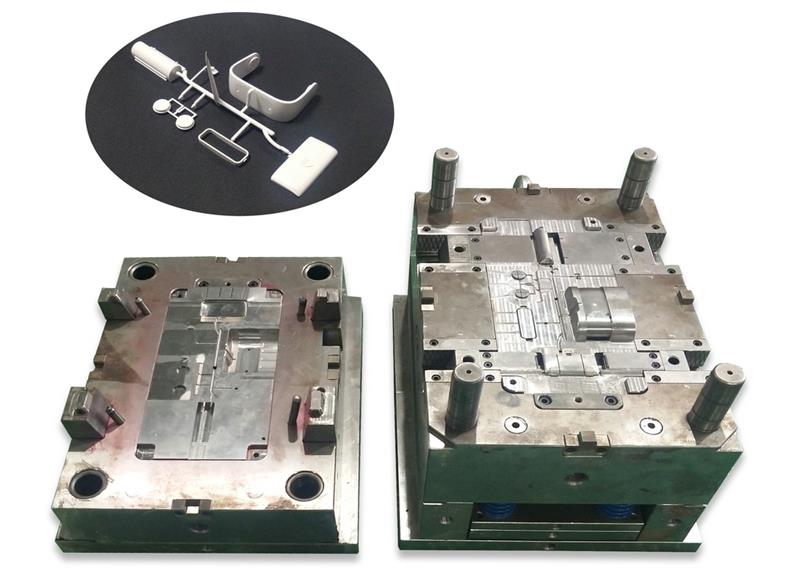
Fig.2 Left is fixed mold and right is the moving mold
During injection, as the nozzle of the injection machine is generally stationary where it connects with the mold, the part of the mold in contact with the injection machine nozzle is termed the fixed mold. On a vertical injection molding machine (with injection from top to bottom), the fixed mold is also known as the upper mold. On a horizontal machine (with injection from left to right or vice versa), it is referred to as the front mold. Correspondingly, the moving mold is known as the lower mold on a vertical machine and the rear mold on a horizontal machine.
The mold cavity of the fixed mold is generally concave since products are typically thin-walled. Therefore, the fixed mold is also called the concave mold or female mold, while the mold cavity of the moving mold is convex, termed the convex mold or male mold.
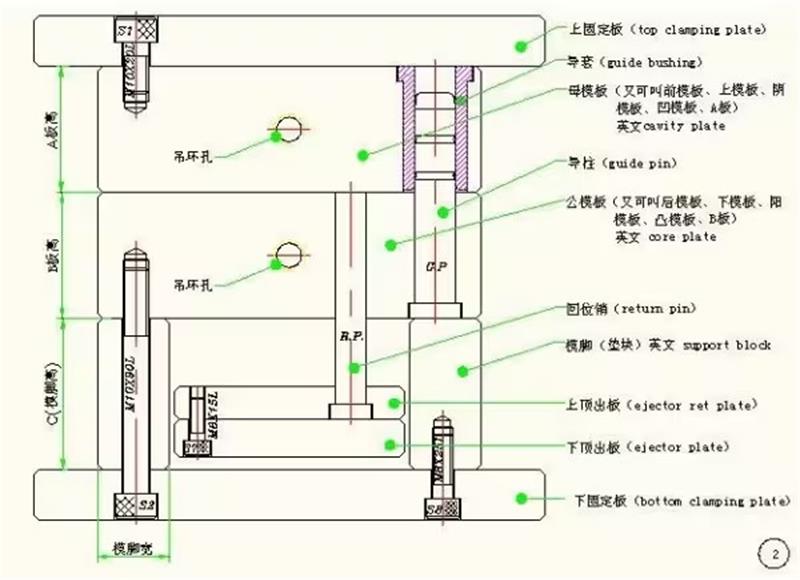
Fig.3 mold structure
Template and Mold Core: The template bears the mold core, containing cooling channels for the product located in the mold cavity after injection. The front and rear mold cores together form the mold cavity, the area filled by the flow of plastic.
Guide Sleeve and Guide Pin: The guide sleeve functions like a sliding bearing, and the guide pin slides in it during the mold opening and closing process, serving as part of the mold's rough positioning system.
Mold Feet: These support the ejection system, including upper and lower ejector plates, ejector pins, return pins, etc.
A, B, C Plates: The mold portion between the front and rear fixed plates generally has a three-stage structure known as A, B, and C plates. For simplicity and cost-saving, standard mold frames are often used for straightforward products, with only the mold cores for different products and some details requiring processing.
During injection molding, the moving and fixed molds close, and dried plastic pellets are poured into the injection molding machine's hopper. The injection machine plunger (screw) pushes the pellets forward, and heating coils in the barrel heat and melt the material into a non-Newtonian fluid. By the time the pellets reach the nozzle, they have become a high-temperature fluid. The molten material is then injected into the mold system through the nozzle as a high-pressure fluid, filling the mold cavity through the main runner, runner, and gate. After filling is complete, the injection stops, and the mold enters the holding phase. Subsequently, the cooling system starts operating, the mold opens, and the ejection system moves to push the product out. Finally, the product is removed.
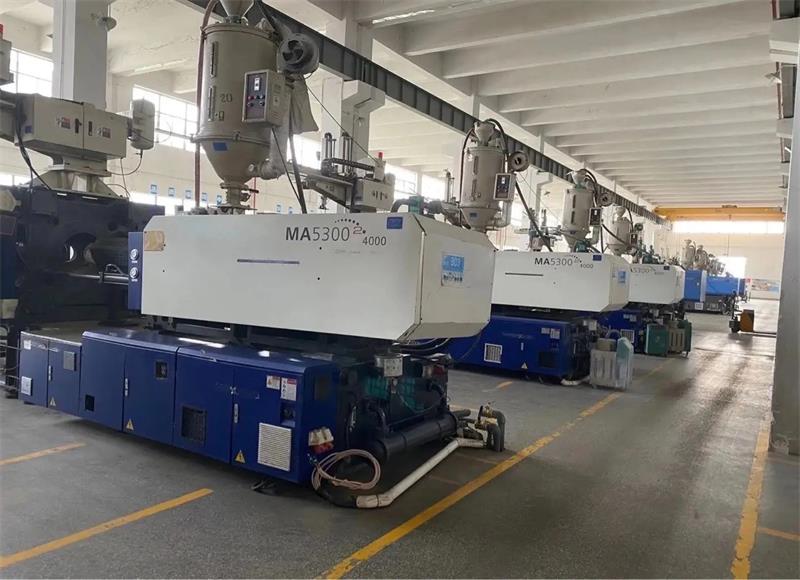

Fig.4 Injection machines
Injection molding is an efficient and rapid production method, typically completing one cycle in less than one minute. This process is not only widely used in plastic products but is also ubiquitous in our daily lives. Understanding the basic structure of molds and the principles of injection molding helps us better comprehend the complexity and precision of this manufacturing process.
 Previous: None
Previous: None
 Next: Photovoltaic Rising Star- The Application and Development of Engineering Plastics
Next: Photovoltaic Rising Star- The Application and Development of Engineering Plastics